Antioxidant
Antioxidants play a crucial role in maintaining the quality and safety of food products.
They are used to prevent the deterioration caused by the oxidation of fats and oils, helping preserve flavor, color, texture, and nutritional value.
By inhibiting the formation of harmful substances such as peroxides and slowing down nutrient degradation, antioxidants contribute to both the shelf life and overall safety of food.
Key Benefits of Antioxidants
1. Ensuring Food Safety
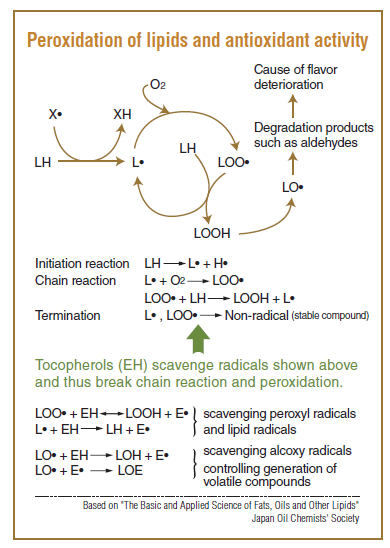
Antioxidants help prevent the formation of harmful substances such as peroxides, which can result from the oxidation of fats. This contributes to maintaining the safety of food products.
2. Efficient Use of Food Resources
By improving shelf life and reducing food waste, antioxidants support the effective utilization of limited food resources.
3. Preserving Food Quality and Nutritional Value
They help prevent the deterioration of flavor and color caused by oxidation, as well as the breakdown of micronutrients such as vitamins.
Types of Antioxidants
Antioxidants can be classified based on their solubility and source:
Water-soluble antioxidants such as Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) and tea extracts
Fat-soluble antioxidants including Vitamin E (tocopherols), BHA, and BHT
Dual-soluble antioxidants like rosemary extract, which dissolve in both water and oil
The effectiveness of an antioxidant depends on the type of food and the specific oxidative process. Proper selection is essential, taking into account factors such as taste, odor, and solubility.
Main Antioxidant Mechanisms (Fat Oxidation)