
Vitamin E
We provide both synthetic and plant-derived forms of vitamin E including a unique synthetic vitamin E derivative that is the only one of its kind in the world.
What is Vitamin E (tocopherol)?
In 1937, Evans successfully extracted vitamin E with the cooperation of the Emerson couple.The name 'tocopherol' comes from the Greek words 'tocos' (to bear children), 'pheros' (to give strength), and 'ol' (alcohol).
Types of Vitamin E
Vitamin E exists in both synthetic and plant-derived forms.
| Absolute Coordination | |||
| 2° | 4° | 8° | |
| α-tocopherol/ RRR-α-tocopherol =d-α-tocopherol | R | R | R |
| Synthetic α-tocopherol/ all-rac-α-tocopherol=dl-α-tocopherol (eight stereoisomers of tocopherol) | R | R | R |
| R | R | S | |
| R | S | R | |
| R | S | S | |
| S | R | R | |
| S | R | S | |
| S | S | R | |
| S | S | S | |
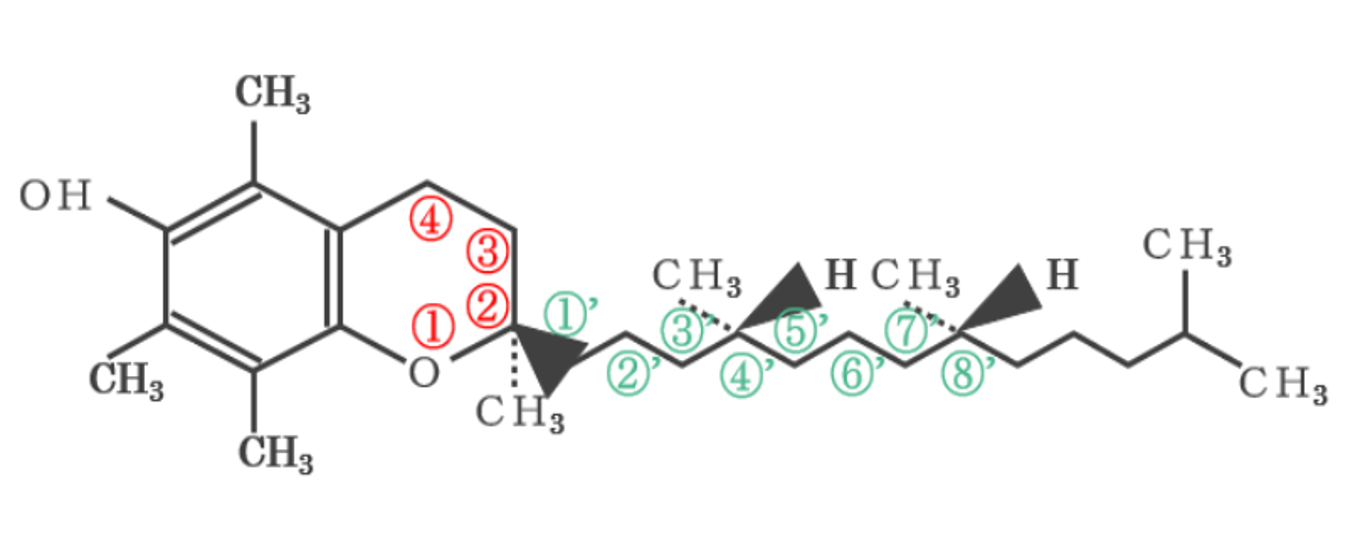
There are four homologs of vitamin E.
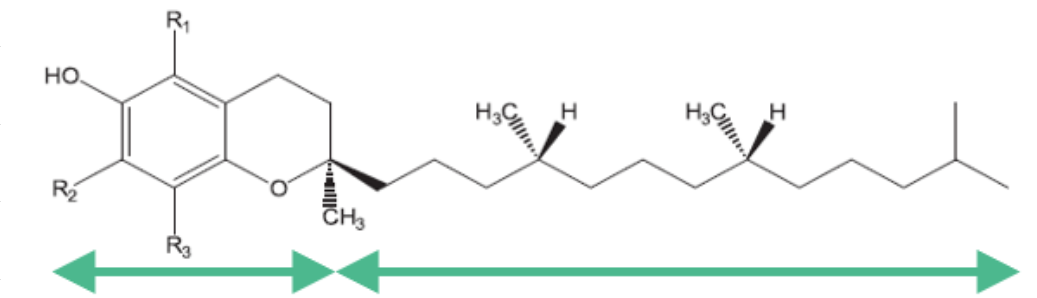
Cromane ring
phytol side chain (There are no unsaturated bonds)
| Compounds | R1 | R2 | R3 |
| α-tocopherol | CH3 | CH3 | CH3 |
| β-tocopherol | CH3 | H | CH3 |
| γ-tocopherol | H | CH3 | CH3 |
| δ-tocopherol | H | H | CH3 |
Antioxidant Properties of Vitamin E
The antioxidant mechanism of vitamin E involves scavenging reactive oxygen radicals.
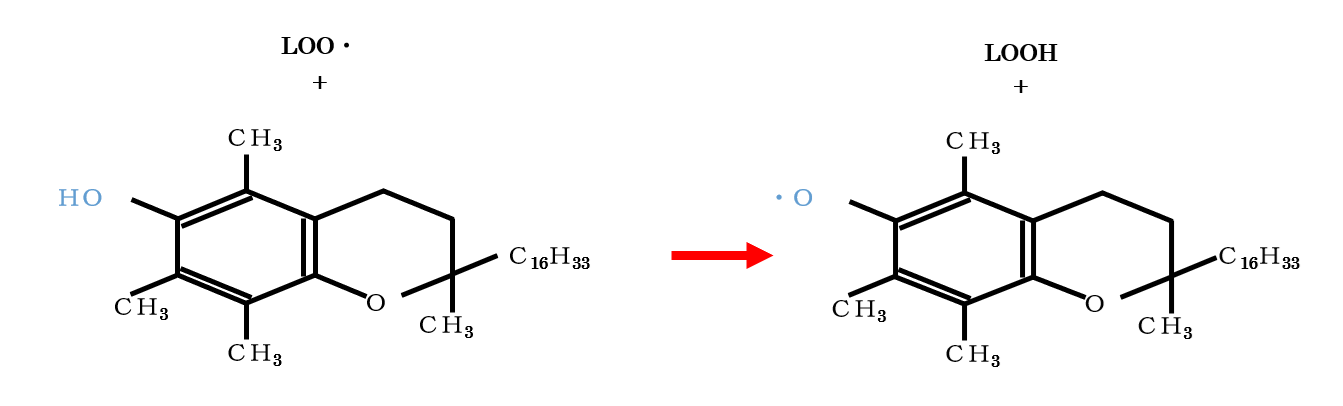
The antioxidant strength of each homolog varies between in vivo and in vitro environments.
In vivo
The transport protein (α-TTP) preferentially transports the alpha form.
The highly reactive alpha form is the most effective.
In vitro (oxidation prevention in food and cosmetics)
The alpha form is highly reactive and is quickly consumed, lacking persistence.
In long-term storage and harsh oxidative conditions, the more stable delta form is the most effective.
Vitamin E
| Product Name | Specification Standard | Package Size (kg) |
| d-δ-Tocopherol | Quasi-drug Ingredient Standard | 1, 5 |
Synthetic Vitamin E
| Product Name | Specification Standard | Package Size (kg) |
| Tocopherol Nicotinate Ester | Japanese Pharmacopoeia | 1, 5 |
| Vitamin E Linoleate Mixture | In-house Standard | 1, 5, 15 |
Tocopherol Nicotinate Ester (EN)
It is one of the B vitamins and has effects such as promoting peripheral blood flow and improving lipid metabolism.
It is a vitamin E derivative formed by esterifying nicotinic acid with vitamin E.
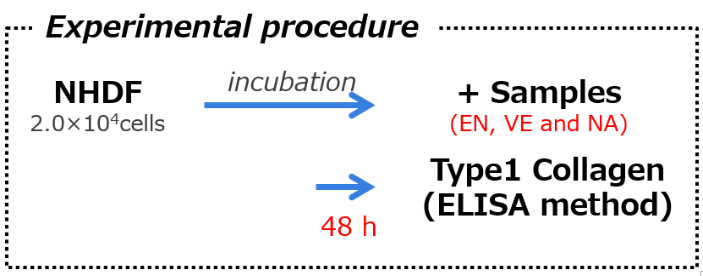
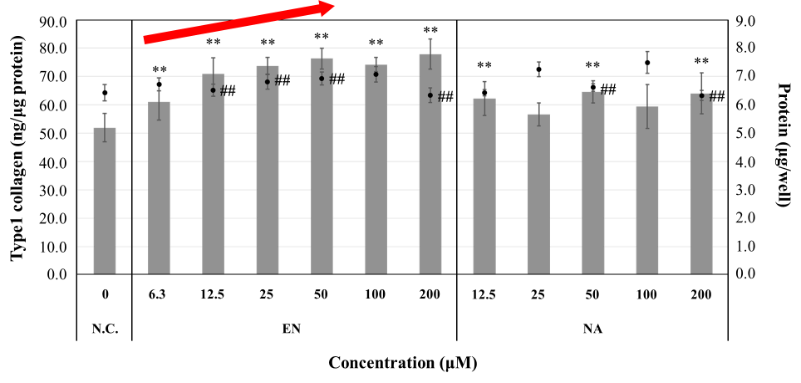
EN increased the synthesis of type I collagen in human dermal fibroblasts (NHDF) in a concentration-dependent manner.
Vitamin E Linoleate Mixture (EL)
It is a vitamin E derivative formed by esterifying linoleic acid, which contributes to ceramide acidity, and tocopherol, which suppresses lipid peroxidation, increased transepidermal water loss, and tissue cell damage.
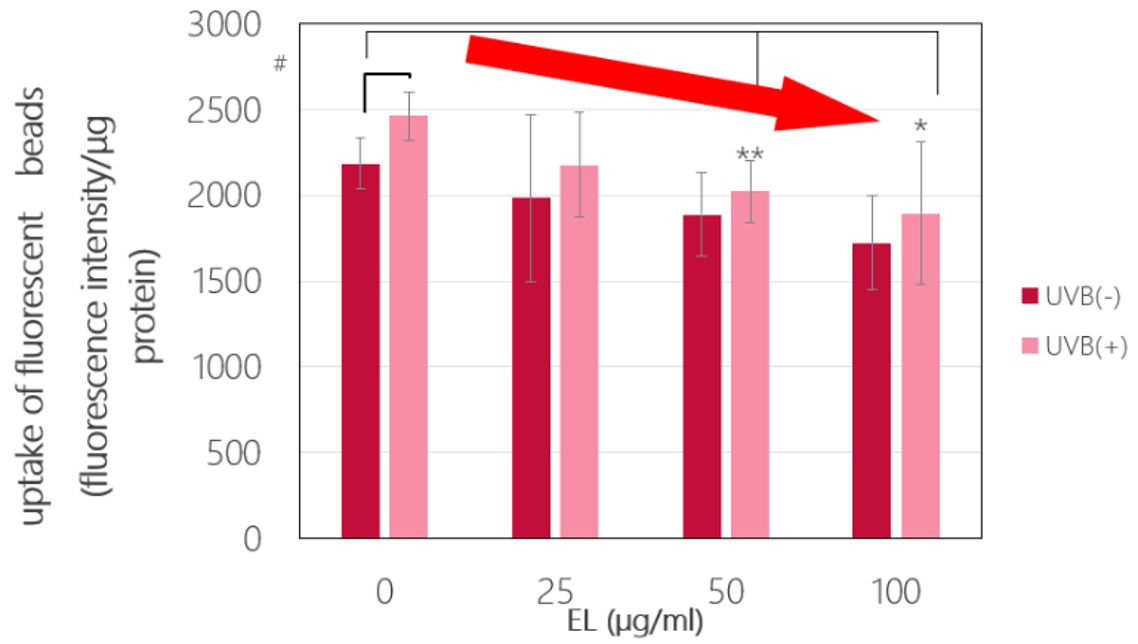
Vitamin E Linoleate Mixture suppressed the UVB-induced increase in uptake of pseudo-melanosomes (fluorescent beads) by HaCaT cells.

